
- info@zebaearth.org

CBG offers a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels. By replacing traditional fuels, it helps mitigate climate change and its detrimental effects.
The use of organic waste for CBG production not only converts waste into valuable fuel but also reduces landfilling and associated environmental pollution.
CBG offers a domestic source of energy, decreasing dependence on imported fossil fuels and enhancing energy security.
The CBG sector presents exciting job creation opportunities in areas like plant operation, waste collection, and transportation.
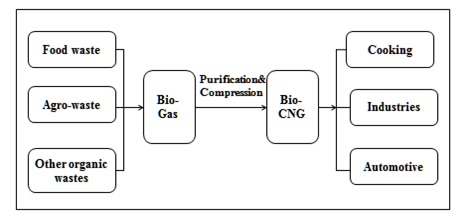
By substituting natural gas and crude oil with CBG, India aims to alleviate its heavy import bills and enhance energy security.
The conversion of agricultural residue and MSW into CBG will significantly mitigate emissions, addressing national climate change commitments.
With only 25% of crop residue currently being utilized, CBG production offers a sustainable alternative to stubble burning, a major air quality concern.
CBG can power vehicles like cars, buses, and trucks, contributing to cleaner transportation and reduced emissions in urban areas.
Industrial facilities can utilize CBG to meet their energy demands, replacing fossil fuels and lowering carbon footprint.
CBG can be injected into natural gas pipelines or used for electricity generation, diversifying the energy mix and promoting renewable sources.
CBG can be used for cooking and heating in homes and commercial establishments, providing a clean and sustainable alternative to conventional fuels.
The CBG sector promises to bolster the rural economy through additional revenue streams for farmers and creating employment opportunities, thereby contributing to the “Swachh Bharat Mission “by promoting responsible waste management.
The government’s commitment is further underscored by the National Policy on Bio-Fuels 2018, which advocates for the advancement of biofuels, including CBG. This policy framework is designed to stimulate investment and innovation in the biofuel sector.
In line with promoting cleaner fuel alternatives, the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has officially sanctioned the use of bio-compressed natural gas (bio-CNG) for vehicles, marking a significant step towards reducing reliance on conventional CNG and fostering a cleaner automotive industry.
The government offers subsidies, grants, and loans to encourage CBG plant establishment and waste-to-wealth creation.
Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation (SATAT) was launched on 1st October 2018 aiming to establish an ecosystem for production of Compressed Bio Gas (CBG) from various waste/ biomass sources in the country. This ambitious scheme aims to establish 5,000 CBG plants by 2024, targeting 15 million metric tonnes (MMT) of annual production. Under SATAT, Oil and Gas Marketing Companies IOCL, BPCL, HPCL, GAIL and IGL have invited Expression of interest (EoI) to procure CBG from potential entrepreneurs for further marketing.
A list of the recent initiatives taken be the Ministry to promote SATAT is as under:
Further Ministry is also engaged with:
The CBG sector in India is brimming with exciting developments:
Focus on rural development: Integrating CBG with rural livelihood programs empowers communities and generates income.
Waste-to-wealth model: Utilizing industrial and agro-industrial waste as feedstock expands resource utilization and promotes circularity.
Technological advancements: Biorefineries integrating CBG production with bioproduct generation offer exciting possibilities.
The CBG sector in India is brimming with exciting developments:
Focus on rural development: Integrating CBG with rural livelihood programs empowers communities and generates income.
Waste-to-wealth model: Utilizing industrial and agro-industrial waste as feedstock expands resource utilization and promotes circularity.
Technological advancements: Biorefineries integrating CBG production with bioproduct generation offer exciting possibilities.
Looking Ahead: A Sustainable Future Fueled by Biogas
With growing government support, innovative technologies, and increasing awareness, India’s CBG sector is poised for exponential growth.
This can lead to: Reduced dependence on fossil fuels and enhanced energy security.
Cleaner air and environment: Lower greenhouse gas emissions contributing to climate change mitigation.
Sustainable waste management: Efficient waste utilization, reducing landfilling and associated pollution.
Economic growth and job creation: Boosting rural and urban economies through diverse opportunities.
By addressing existing challenges and capitalizing on these opportunities, India can truly realize the potential of CBG and create a more sustainable future fueled by this clean and renewable energy source.








We provide a start to finish solution that converts organic waste into BioCNG and organic manure/soil conditioner that results in increased industrial and farmer productivity and a cleaner environment.